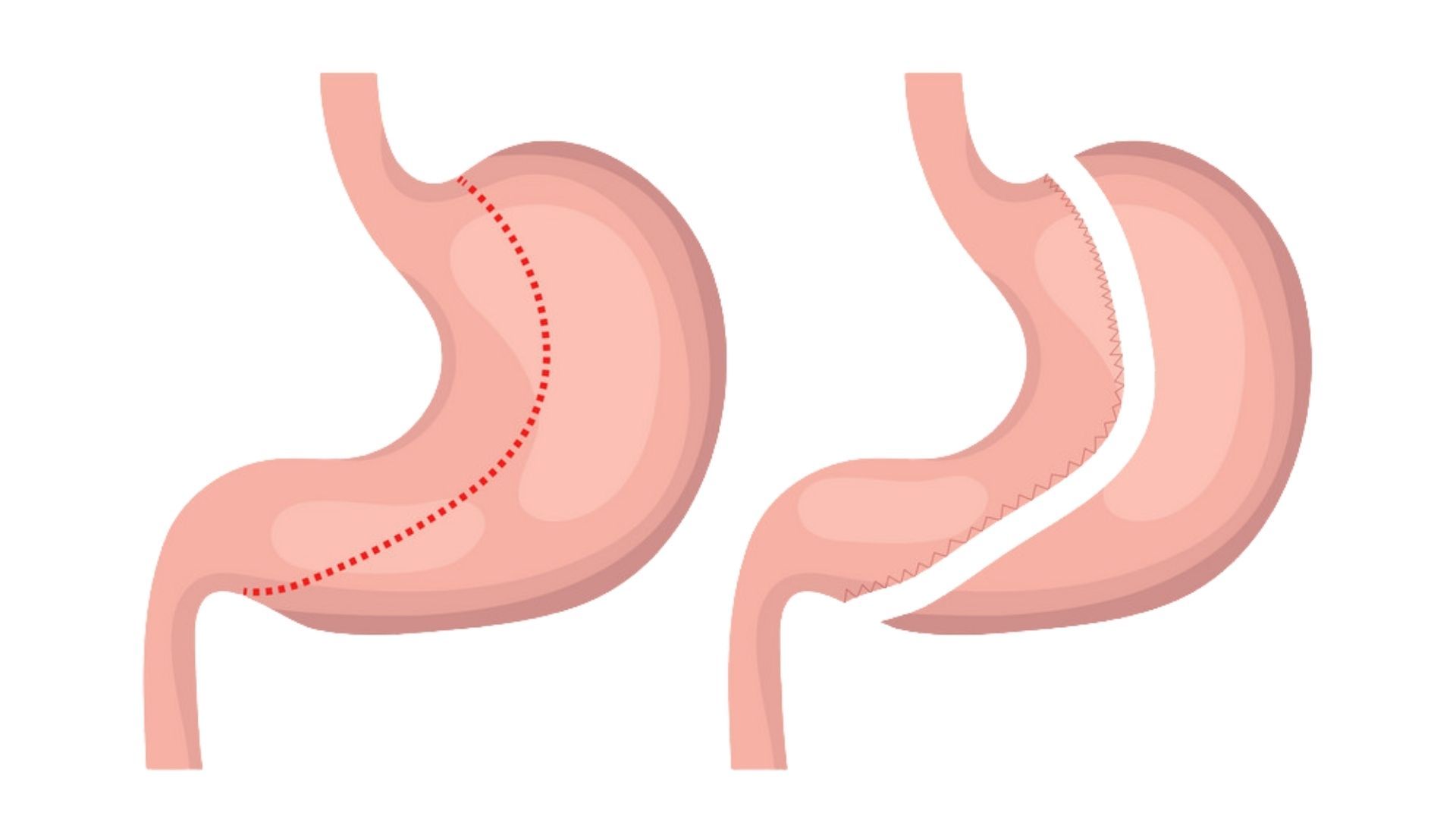
In recent years, هزینه عمل اسلیو معده surgery has gained popularity as an effective treatment for obesity and related health issues. Also known as sleeve gastrectomy, this surgical procedure involves reducing the size of the stomach to promote weight loss. Despite its proven success and increasing acceptance within the medical community, gastric sleeve surgery remains shrouded in myths and misconceptions. Let’s delve into some of the most common misconceptions surrounding this procedure and separate fact from fiction.
Myth 1: Gastric Sleeve Surgery is the Easy Way Out
One of the most pervasive myths about gastric sleeve surgery is that it represents the “easy way out” for individuals struggling with obesity. This notion couldn’t be further from the truth. Opting for gastric sleeve surgery is a significant decision that requires thorough evaluation, commitment, and lifestyle changes.
Individuals who undergo gastric sleeve surgery must adhere to a strict pre-operative and post-operative regimen, including dietary modifications, exercise routines, and regular medical follow-ups. Moreover, the surgery itself carries risks and potential complications, as with any major surgical procedure. It’s essential to recognize that gastric sleeve surgery is not a shortcut to weight loss but rather a tool to support individuals in their journey towards better health.
Myth 2: Gastric Sleeve Surgery is Dangerous
While all surgical procedures come with inherent risks, gastric sleeve surgery is generally considered safe when performed by experienced surgeons in accredited medical facilities. Advances in surgical techniques and technology have significantly reduced the risks associated with the procedure.
The mortality rate for gastric sleeve surgery is low, especially compared to the risks associated with untreated obesity and its associated health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. As with any medical intervention, it’s crucial for patients to undergo a comprehensive pre-operative evaluation to assess their suitability for surgery and to discuss potential risks and benefits with their healthcare team.
Myth 3: Gastric Sleeve Surgery is Only About Weight Loss
While weight loss is a primary goal of gastric sleeve surgery, its benefits extend far beyond shedding excess pounds. Many individuals who undergo sleeve gastrectomy experience improvements in obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and joint pain.
By reducing the size of the stomach, gastric sleeve surgery helps to limit food intake and promote feelings of satiety, making it easier for patients to adopt healthier eating habits and maintain long-term weight loss. Additionally, weight loss achieved through gastric sleeve surgery can lead to enhanced self-esteem, increased mobility, and a better quality of life overall.
Myth 4: Gastric Sleeve Surgery is Reversible
Unlike some other bariatric procedures, such as gastric banding, gastric sleeve surgery is not reversible. During the procedure, a portion of the stomach is permanently removed, leaving behind a smaller, banana-shaped sleeve. Once this alteration is made, it cannot be undone.
While gastric sleeve surgery offers significant and sustainable weight loss for many patients, it’s essential to consider the irreversible nature of the procedure before making a decision. Patients should undergo thorough counseling and education to fully understand the implications of gastric sleeve surgery and explore alternative treatment options if necessary.
Myth 5: Gastric Sleeve Surgery is Only for Morbidly Obese Individuals
While gastric sleeve surgery is often recommended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher (considered morbidly obese) or a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions, it may also be suitable for those with lower BMIs who have not achieved success with nonsurgical weight loss methods.
Candidates for gastric sleeve surgery undergo a comprehensive evaluation to assess their overall health, weight loss history, and readiness for surgery. Factors such as age, medical history, and lifestyle habits are taken into account to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for each individual.